Case 2: A 53-Year-Old Woman Who Presents With Fever
This 53-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 10 day history of general malaise, fever, and chills. Over the past 24 hours, she reports developping persistent right upper quadrant abdominal pain. An abdominal CT is performed – what finding explains her presentation?
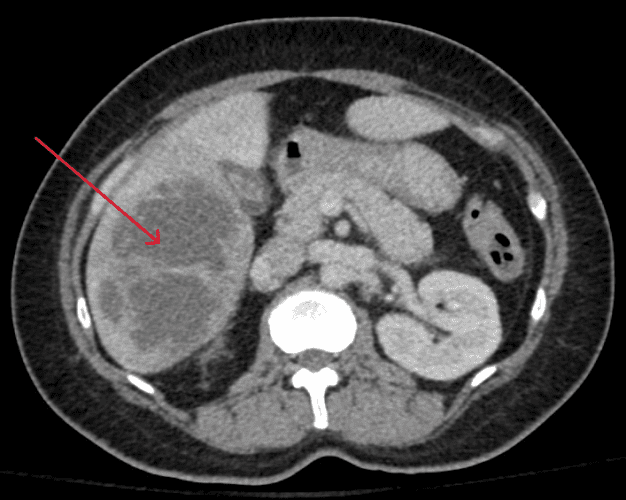
When combined with her clinical history, the bilobed hypoattenuating complex in the right lobe of her liver (red arrow) is highly suspicious for a pyogenic abscess.

A hepatic abscess is a localized collection of pus, and can be bacterial, parasitic, or fungal. In the case of pyogenic liver abscesses, the most common causative organisms are Escherichia coli, Streptococcus species, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Enterococcus species. Typically, these bacteria arise from gastrointestinal tract flora, however hematogenous spread should be suspected when Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species are isolated.
Infections of the biliary tree currently account for the majority of pyogenic liver abscesses, related to malignant obstruction, instrumentation of the biliary ducts, or gallstones. Seeding of the portal vein can also occur via intra-abdominal infections (ex. appendicitis, diverticulitis), gastrointestinal tumours, inflammatory bowel disease, or hematogenous spread in patients with bacteremia. Approximately 35% of pyogenic liver abscesses are cryptogenic (particularly those caused by Klebsiella), with no identifiable cause.
Radiographic Findings:
Due to preferential portal vein flow, most liver abscesses are found in the right hepatic lobe, as in this case. Most pyogenic liver abscesses are hypoechoic, and appear as solitary lesions with septations. Early lesions have poorly defined irregular contours (such as in this case), while more developed lesions have clearly delineated rounded contours:
Amebic liver abscesses (caused by Entamoeba histolytica), are rare, but also present with fever and right upper quadrant pain, and typically occur in immigrants and travellers. They can be differentiated from pyogenic liver abscesses on imaging as they appear as a rounded, homogeneous, hypoechoic lesions that are usually located near the liver capsule:
Source: Roediger R, Lisker-Melman M. Pyogenic and Amebic Infections of the Liver. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020 Jun;49(2):361-377. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.01.013. PMID: 32389368. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32389368/
Under ultrasound guidance, a pigtail catheter was inserted, which drained purulent fluid, positive for Klebsiella.


Blood cultures also grew Klebsiella in two of two vials:


Based on her culture susceptibilities, her antibiotics were stepped down to ciprofloxacin, and a repeat ultrasound five days after pigtail catheter insertion demonstrated complete resolution of the abscess.
No biliary abnormalities were detected on imaging, and a colonoscopy was normal. Thus, her liver abscess was presumed to be cryptogenic, as is commonly the case when Klebsiella is isolated on cultures.